How to conjugate estar
Estar (Meaning: To be) is one of the most important verbs in the Spanish language. The conjugation of estar in the present tense is: Yo estoy (I am), tú estás (you are), él/ellá/usted está (he/she is, you are), nosotros estamos (we are), vosotros estáis (you are) and ellos/ellas/ustedes están (they/you are).

Estar is an irregular AR verb. This means that when conjugated in the present tense, it’s endings are different than other regular AR verbs, such as hablar (to speak).
This page on our site covers the hablar conjugation charts in detail and this page covers AR verbs in detail.
Estar conjugation in the present tense

To be in Spanish explained
Estar and ser both mean “to be” in Spanish. The language uses estar to describe temporary states such as feelings and location, while it uses ser to describe more permanent states such as one’s nationality, profession and physical characteristics.
This page on our site examines the differences between ser and estar in detail while this page provides detailed conjugation charts for ser.
Further down the page we provide conjugation charts with example sentences for estar in the following eight commonly used verb tenses:
- Present tense (presente de indicativo)
- Near future (futuro inmediato)
- Future tense (futuro)
- Preterite (pretérito)
- Present perfect indicative (perfecto de indicativo)
- Imperfect (imperfecto de indicativo)
- Conditional (potential simple)
- Present subjunctive (presente de subjuntivo)
Estar conjugation table
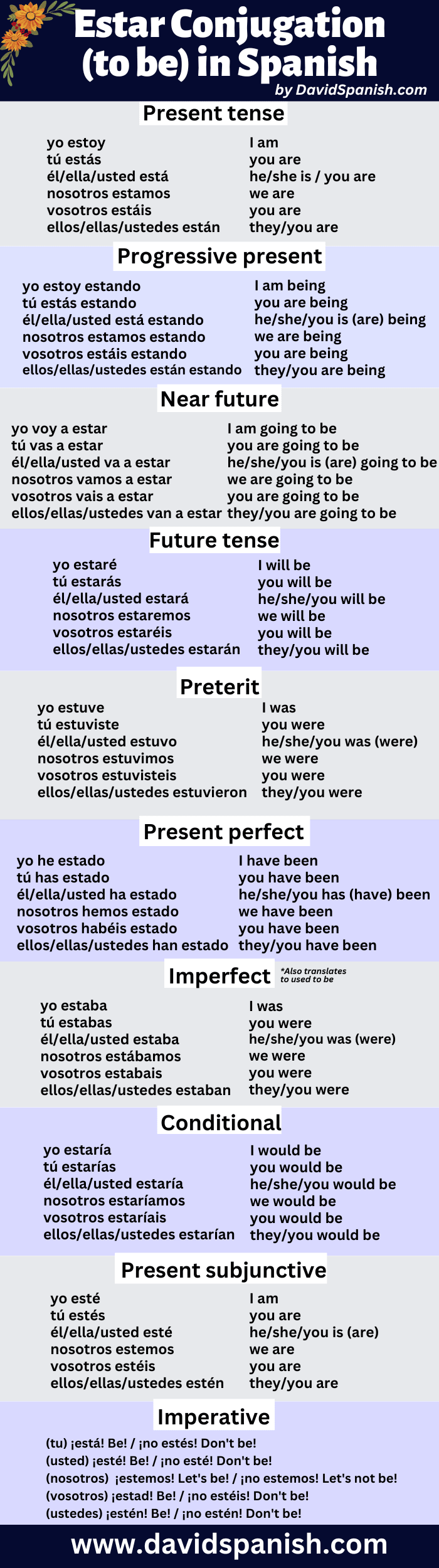
Forms of estar at a glance
The following graphic covers the verb estar in twelve tenses in the first-person singular (yo) form.

Estar conjugation charts
Present tense (presente de indicativo)
In the present tense, yo estoy translates to “I am”. As stated above, estar is mainly used for temporary states: emotions and locations.
| yo estoy | I am | Yo estoy en la casa. | I am at home. |
| tú estás | you are | Tú estás a Guadalajara. | You are in Guadalajara. |
| él/ella, usted está | he/she is; you are | Él está trabajando. | He is working. |
| nosotros estamos | we are | Nosotros estamos cansados. | We are tired. |
| vosotros estáis | you are | Vosotros estáis satisfechos. | You are full. |
| ellos/ellas, ustedes están | they/you are | Ellos están comiendo. | They are eating. |
Near future (futuro inmediato)
The near future tense is formed with the following construction: present tense of ir (to go) + preposition a + infinitive. For example, yo voy a estar translates to “I’m going to be”.
| yo voy a estar | I'm going to be | Yo vo a estar cansado. | I'm going to be tired. |
| tú vas a estar | you're going to be | Tú vas a estar feliz. | You're going to be happy. |
| él/ella, usted va a estar | he/she's going to be; you're going to be | Él va a estar emocionado. | He's going to be thrilled. |
| nosotros vamos a estar | we're going to be | Nosotros vamos a estar pendientes. | We are going to be on the look out. |
| vosotros vais a estar | you're going to be | Vosotros vais a estar de vuelta. | We are going to be back. |
| ellos/ellas, ustedes van | they/you're going to be | Ellos van a estar ocupados. | They are going to be busy. |
Future tense (futuro)
In the future tense, yo estaré translates to “I will be”.
| yo estaré | I will be | Yo estaré con ustedes. | I'll be with you. |
| tú estarás | you will be | Tú estarás en la escuela. | You'll be in school. |
| él/ella, usted estará | he/she/you will be | Ella estará sana. | She'll be in good health. |
| nosotros estaremos | we will be | Nosotros estaremos enamorados. | We will be in love. |
| vosotros estaréis | you will be | Vosotros estaréis enojados. | You'll be angry. |
| ellos/ellas, ustedes estarán | they/you will be | Ellos estarán orgulloso de su éxito. | They'll be proud of your success. |
Preterite (pretérito)
The preterite is a commonly used past tense for completed actions. Yo estuve translates to “I was”.
| yo estuve | I was | Yo estuve a Madrid. | I was in Madrid. |
| tú estuviste | you were | Tú estuviste muy feliz. | You were very happy. |
| él/ella, usted estuvo | he/she was; you were | Él estuvo a Buenos Aires. | He was in Buenos Aires. |
| nosotros estuvimos | we were | Nosotros estuvimos en la casa. | We were at home. |
| vosotros estuvisteis | you were | Vosotros estuvisteis en la oficina. | You were at the office. |
| ellos/ellas, ustedes estuvieron | they/you were | Ellos estuvieron juntos. | They were together. |
Present perfect indicative (perfecto de indicativo)
The present perfect is a commonly used Spanish past tense which is used to express past actions which have a bearing on the present. It is formed by combining the present tense of haber (to have) with past participle. Yo he estado translate to “I have been”.
| yo he estado | I have been | Yo he estado muy ocupado este mes. | I've been very busy this month. |
| tú has estado | you have been | Tú has estado trabajando en California. | You've been working in California. |
| él/ella, usted ha estado | he/she has been; you have been | Él ha estado bendito. | He's been blessed. |
| nosotros hemos estado | we have been | Nosotros hemos estado muy felices. | We've been very happy. |
| vosotros habéis estado | you have been | Vosotros habéis estado en España desde hace un año. | You've been in Spain for one year. |
| ellos/ellas, ustedes han estado | they/you've been | Ellos han estado en contacto últimamente. | They've been in touch recently. |
Imperfect (imperfecto de indicativo)
The imperfect tense is another commonly used Spanish past tense used to describe actions occurred over time at non-specified times. Yo estaba translates to “I was” or “I used to be”.
| yo estaba | I was, used to be | No vine porque estaba cansado. | I didn't come because I was tired. |
| tú estabas | you were, used to be | ¿Dónde estabas? ¡Te llamé tres veces! | Where were you? I called you three times! |
| él/ella, usted estaba | he/she was, used to be; you were, used to be | ¿Por qué estaba tan enojado? | Why was he so angry? |
| nosotros estábamos | we were, used to be | Nosotros estábamos muy contentos con los resultados. | We were very pleased with with the results. |
| vosotros estabais | you were, used to be | Vosotros estabais muy tímidos. | You used to be very shy. |
| ellos/ellas, ustedes estaban | they/you were, used to be | Ellos estaban el centro cuando llegué. | They were downtown when I arrived. |
Conditional (potential simple)
The conditional tense is used to describe hypothetical actions. Yo estaría translates to “I would be”.
| yo estaría | I would be | Yo estaría feliz si ayudaras. | I'd be happy if you helped. |
| tú estarías | you would be | Tú estarías más tranquilo si tuverias más tiempo libre. | You'd be more at ease if you had more free time. |
| él/ella, usted estaría | he/she/you would be | Él estaría más feliz si tuviera una novia. | He's be happier if he had a girlfriend. |
| nosotros estaríamos | we would be | Nosotros estaríamos listos si tuviéramos más tiempo. | We'd be ready if we had more time. |
| vosotros estaríais | you would be | Vosotros estaríais con nosotros si no estuvieran con ellos. | You'd be with us if you weren't with them. |
| ellos/ellas, ustedes estarían | they/you would be | Ellos estarían celosos supieran como estoy viviendo. | They'd be jealous if they knew how I'm living. |
Present subjunctive (presente de subjuntivo)
The subjunctive mood is used to express wishes, emotions and doubts. Yo esté translates to “I am”. Que esté can translate to “that I be”.
| yo esté | I am | Quiere que esté más serio en la vida. | He wants me to be more serious in life. |
| tú estés | you are | Es importante que estés listo. | It's important that you be ready. |
| él/ella, usted esté | he/she is, you are | No pieno que él esté disponible. | I don't think he's available. |
| nosotros estemos | we are | No piensa que estemos felices. | He doesn't think we're happy. |
| vosotros estéis | you are | Es dudoso que estéis a Valencia. | It's doubtful that you're in Valencia. |
| ellos/ellas, ustedes estén | they/you are | Es necesario que estén puntuales. | It's required that they be on time. |
Discover more:
- Hacer (to make, do) conjugation charts
- Tener (to have) conjugation charts
- Spanish ER verbs
- Spanish IR verbs
- La Bamba Meaning, Spanish Lyrics & English Translation - May 4, 2024
- Bésame Mucho Meaning, Spanish Lyrics & English Translation - May 3, 2024
- Querida – Lyrics, Meaning & Translation - May 2, 2024
